Human resources compliance is the foundation of a fair, safe, and equitable workplace. It ensures your company follows the law, protects employees, and reduces risk. A strong compliance strategy also provides clear guidance for HR teams when ethical issues come up.
As companies face new compliance burdens, consistent, documented policies are more important than ever. Artificial intelligence (AI) use is widespread, and HR teams need to spearhead responsible use and stay on top of new laws governing its use. Employees need reliable, up-to-date guidelines they can reference as new regulations roll out and expectations evolve.
This guide explains what HR compliance is and why it matters. You’ll learn how an effective HR compliance checklist keeps your team organized and audit-ready for 2026. Then, download the HR Compliance Checklist to help review your processes, refresh your employee handbook, and safeguard your company.
What Is HR Compliance?
HR compliance involves creating, enforcing, and updating company policies that comply with labor and employment laws and regulations. Your HR team is responsible for keeping policies updated as laws change or regulations expand. HR professionals also help enforce company policies and take action to fix noncompliance.
HR teams also review and manage AI tools used for recruiting and other people management tasks to make sure they are fair and follow the law. Often, you’re also in charge of creating a responsible AI use policy,
Why Is HR Compliance Important?
Following all federal, state, and local laws is absolutely essential. It shapes your company culture and impacts its reputation and the employee experience. Thorough compliance protects your company against legal action and financial liability that can result from noncompliance.
Compliance keeps the work environment safe and ensures that every employee is treated fairly. Many laws that govern how businesses operate protect workers’ rights:
- Workplace safety regulations help protect employees from injury.
- Anti-harassment laws stop bullying, discrimination, and other harmful behaviors.
- Anti-discrimination laws prevent bias based on protected characteristics like race, gender, or age.
- Pay and wage laws ensure employees are paid fairly and protect them from wage theft.
HR compliance helps your company run smoothly by streamlining processes and minimizing errors or fines. Compliant procedures can help you avoid costly mistakes and make adjustments if and when regulations change. HR compliance issues can lead to serious consequences, including fines, license revocation, and even prison time.
Violating laws is a significant financial risk — and an even bigger risk to your reputation. Infractions can generate negative publicity and damage your brand. HR compliance plays a starring role in establishing your company as a fair, ethical employer. As AI becomes part of HR workflows, compliance helps prevent unfair bias in automated systems and requires human review of AI-driven decisions.
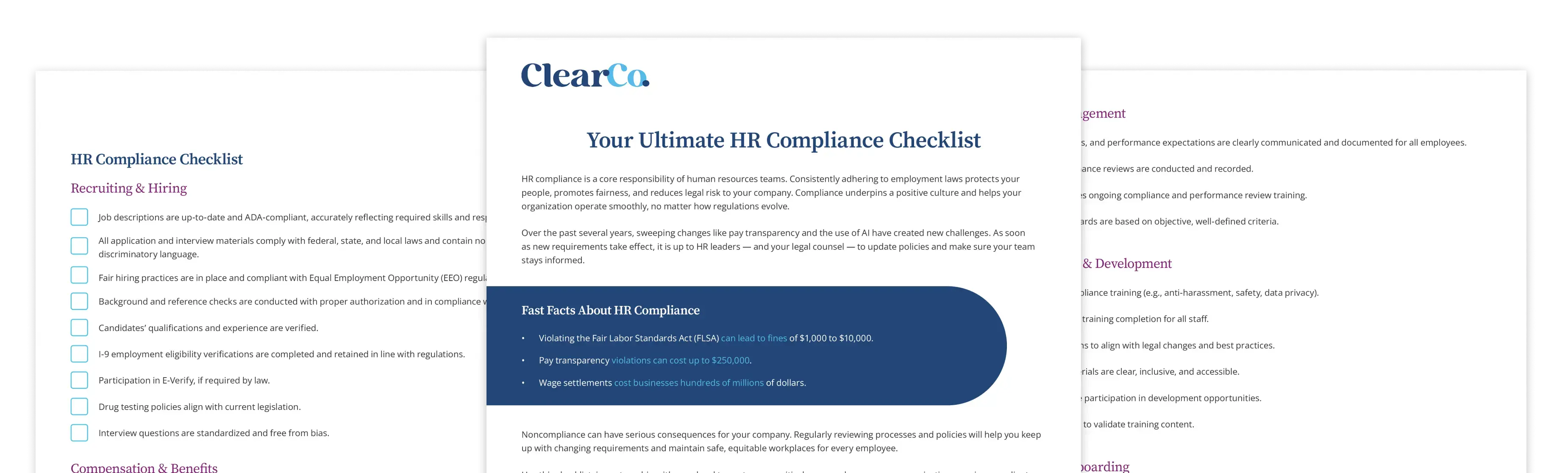
Fast Facts About HR Compliance
- Violating the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) can lead to fines of $1,000 to $10,000.
- Pay transparency violations can cost up to $250,000.
- Wage settlements cost businesses hundreds of millions of dollars.
HR Employment Laws To Know
The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) administers and enforces many federal laws that businesses must follow. Those include well-established worker protections and new rules around pay disclosure and overtime.
Other enforcement agencies include:
- State DOLs
- Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
- U.S Department of Justice
- Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA), a division of the DOL
Prominent Employment Laws
- Title VII of the Civil Rights Act: Protects employees from discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. Title VII covers workers regardless of their employee classification (full-time, part-time, or independent contractor).
- Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA): Sets rules for minimum wage, overtime pay, and child labor protections. It also defines employee classifications and sets guidelines for independent contractors.
- Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA): Requires employers to provide a safe work environment for all workers, including independent contractors.
- Equal Pay Act (EPA): Requires equal pay for equal work, regardless of gender.
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): Protects employees with disabilities and requires reasonable accommodations.
- Affordable Care Act (ACA): Requires companies with 50+ employees to provide affordable health insurance and follow rules on employee benefits, disclosure, and open enrollment.
- Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA): Allows eligible employees up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave for medical or family reasons, while protecting their benefits.
New HR Compliance Rules
- Pay Transparency: Laws requiring wage disclosure in job descriptions are expanding. By mid-2026, pay transparency laws will be in effect in 16 U.S. states and Washington, D.C.
- New FLSA requirements: Salary thresholds for overtime increased to $58,656 as of January 2025, with adjustments every three years starting in 2027.
- California AI Rules: As of October 1, 2025, employers must follow new FEHA regulations for using AI in hiring and employee decisions. This includes testing AI tools for bias, keeping records for four years, and providing human oversight of AI decisions.
How To Keep HR Compliance on Track
Staying compliant requires regular audits and systematic tracking. Many HR teams struggle because they lack systems in place to verify that they've covered all bases. That's where an HR compliance checklist becomes essential.
A well-structured checklist helps you:
- Catch gaps before they become problems: Regular reviews reveal missing documentation or outdated policies.
- Onboard team members faster: Compliance requirements are clear for HR and easy to understand for new hires.
- Prepare for audits confidently: When you've addressed every area, audits become routine.
- Protect your organization: Documented compliance processes demonstrate good faith efforts.
- Stay current: Regular checklist reviews prompt policy updates when laws change.
HR Compliance Best Practices
Strong compliance isn’t just about the rules you put on paper. It’s about how they show up in your HR habits. A few good habits can make all the difference for staying audit-ready and protecting your team.
- Document everything: Track training, handbook acknowledgments, and background checks.
- Stay current: Set regular times to review new laws and update your policies.
- Use technology: HR software keeps compliance tasks, reviews, and reminders organized. Regularly audit AI tools for bias and accuracy, and train your HR team on how to monitor AI decisions responsibly.
- Train often: Give managers and staff practical training so they know what’s expected and how to spot issues.
Building these best practices into your workflow helps you catch problems early and makes compliance a lot less stressful.
Your HR Compliance Checklist
Compliance is an ongoing process and a key part of any strong HR strategy. Regularly reviewing your policies with your legal team ensures you stay compliant — and get ahead of new rules that could affect you.
To make staying audit-ready easier, we created the HR Compliance Checklist. It covers critical areas like:
- Recruiting and Hiring
- Compensation and Benefits
- Performance Management
- New: Training and Development
- Termination and Offboarding
- New: Using AI in HR
Keep your employees safe, your processes fair, and your company protected. Download ClearCompany’s HR Compliance Checklist and start your process audits now.

.png)
